Soil microbial communities in grasslands – Biogeography at the local and regional scale
Whereas temporal patterns of soil microbial abundance and function are well known for different agricultural ecosystems, it was not clear whether the spatial distribution of soil organisms is constant within a season. Therefore, it was interesting to know whether the spatial distance of different taxa and different soil microbial processes change during a vegetation period. Interactions of microorganisms with their micro-environment might have consequences for their functioning at the plot scale. For example, high sensitivity of specific bacterial taxa to drought would increase the spatial distance between these microorganisms in summer, whereas drought tolerance of other bacterial taxa could induce a rather constant pattern of these tolerant microorganisms. At the level of community functioning, the local stability of enzymes could induce seasonal shifts in local degradation of different substrates. Seasonal pattern of biogeography need to be tested at the molecular, cellular and community levels.
This study provided a platform for different Biodiversity Explorers to clarify the spatial and temporal distribution of soil bacteria, genetic structure of bacterial populations and their functions at grassland sites under different land-use intensities. During the first phase (2008 -2011) of the project we focused on spatial patterns of chemical and biological properties at a scale of 10 x 10 m2 using nine plots from each exploratory (VIP). During the second phase (2011-2014) we extended our concept and invited colleagues with different expertise in soil ecology and molecular microbiology to broaden our research at this scale. The most important goal was to investigate whether seasonal changes in biotic and abiotic factors modify the biogeography of soil microorganisms at the plot scale (10 x 10 m2).
We hypothesized that (i) by a temporally and spatially intensive examination of an unimproved grassland at the plot scale (10 m x 10 m) we could distinguish spatial changes in microbial biogeography, and (ii) this sampling approach would clarify the degree to which the microbial spatial structures we observed could be correlated with stages of plant growth and soil abiotic properties. We expected also to gain insight into the persistence of microbial spatial structure and the relationships of microbial communities with their environment.
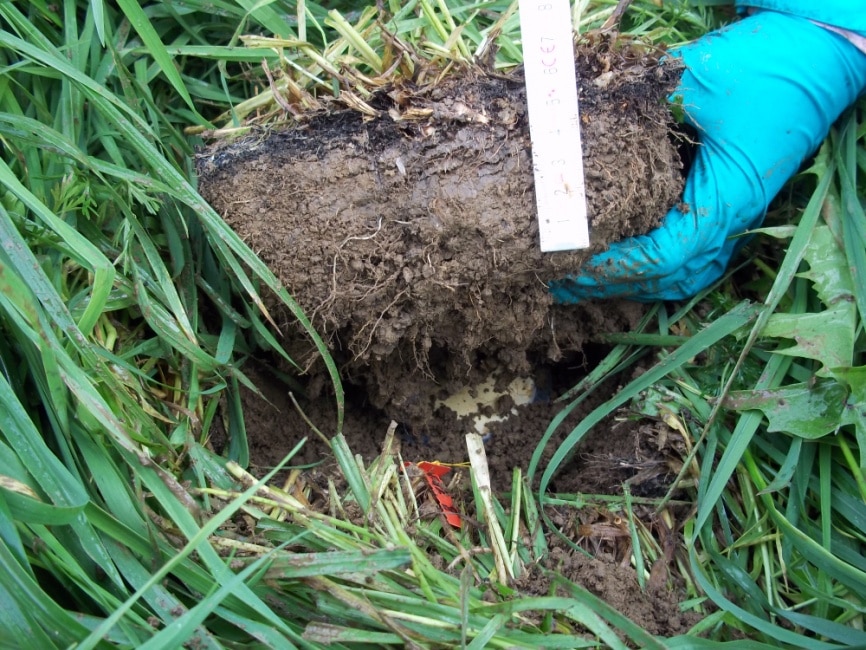
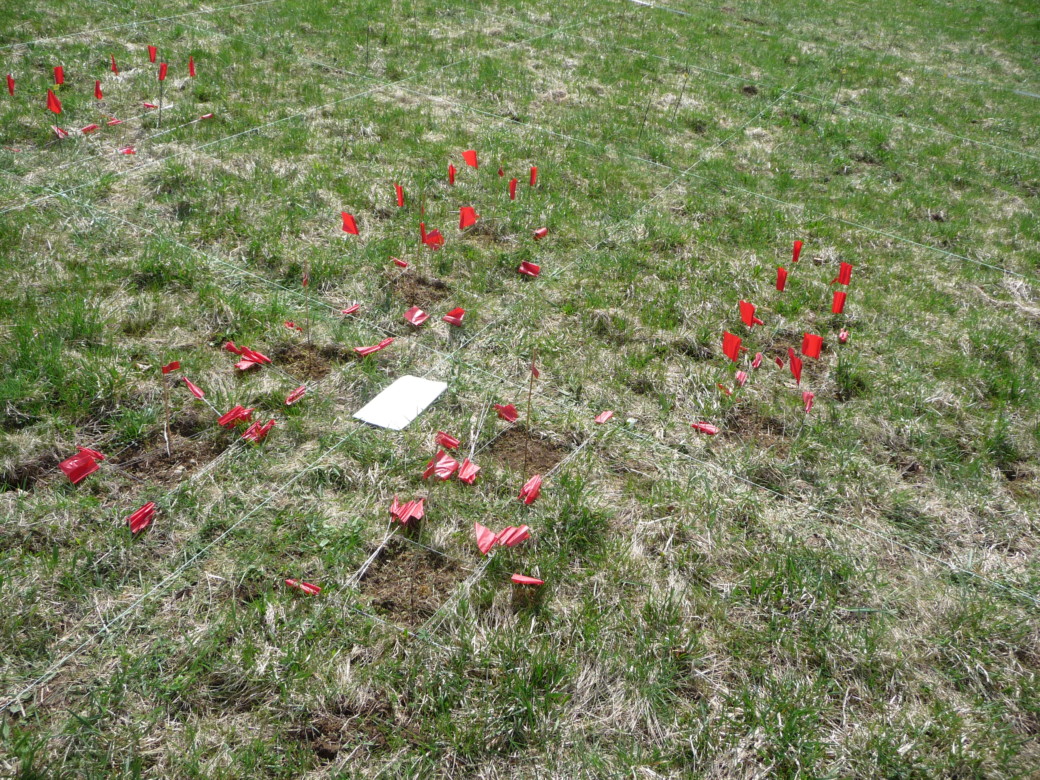
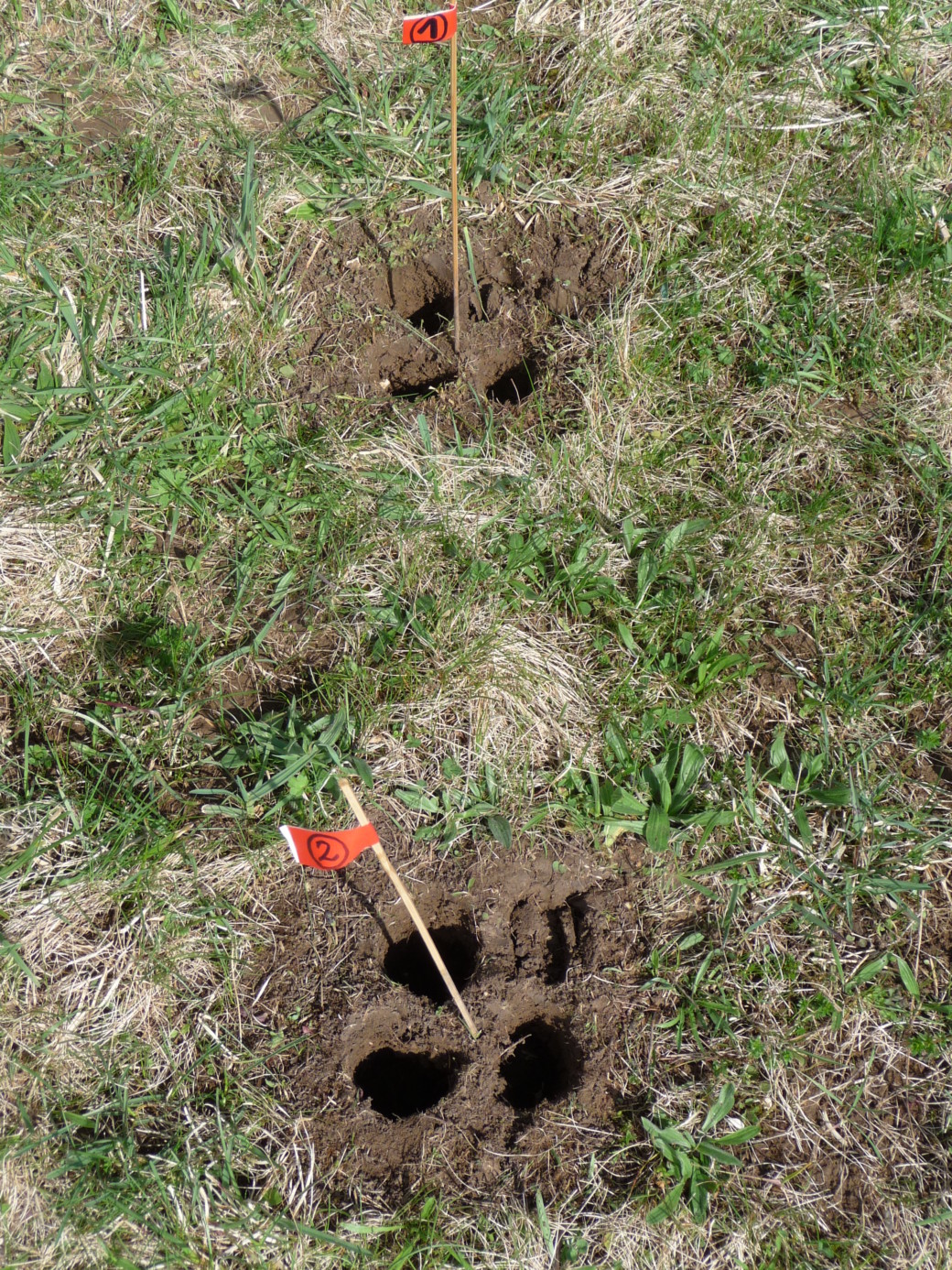
Soil sampling was performed on one low land-use intensity grassland in the Schwäbische Alb (AEG31) at six times within one season to cover the following stages of substrate release from plant communities: at the beginning of the vegetation period, during the main growth phase, at around peak plant biomass, two weeks after the grassland was mown, nine weeks after mowing and two weeks after it was lightly grazed, and after the first frost. At each sampling date we have chosen 60 points for local estimation of plant community composition and for soil sampling. The total number of 60 samples guarantees that we had a minimum of 30 pairs of short lag distances (min. 50 cm). Members of the group of D. Prati (Bern) was responsible for quantification of plant biomass, relative abundance, and developmental stage of plants within an area around each sampling point (20 x 20 cm). The central part of this area was used for soil sampling using a soil corer (58 mm diameter) to a depth of 10 cm.
The multidisciplinary approach allowed elucidating the spatio-temporal variation of functional traits and diversity of plants, animals and microorganisms at different taxonomical levels (please see list of publications below).
Microbial community spatial structure was positively correlated with the local environment, i.e. physical and chemical soil properties, in spring and autumn, while the density and diversity of plants had an additional effect in the summer period (Regan et al. 2014, 2015). Spatial relationships among plant and microbial communities were detected only in the early summer and autumn periods when aboveground biomass increase was most rapid and its influence on soil microbial communities was greatest due to increased demand by plants for nutrients. Individual properties exhibited varying degrees of spatial structure over the season. Differential responses of Gram positive and Gram negative bacterial communities to seasonal shifts in soil nutrients were detected. We concluded that spatial distribution patterns of soil microorganisms change over a season and that chemical soil properties are more important controlling factors than plant density and diversity.
Presenting N cycling microorganisms as an example, we revealed that the seasonal changes in abundances of marker genes for total archaea and bacteria (16S rRNA), nitrogen fixing bacteria (nifH), ammonia oxidizing archaea (amoA AOA) and bacteria (amoA AOB), and denitrifying bacteria (nirS, nirK and nosZ) were associated with changes in substrate availability associated with plant growth stages (Regan et al. 2017). Potential nitrification and denitrification enzyme activities were strongly spatially structured at the studied scale, corresponding to periods of rapid plant growth, June and October, and their spatial distributions were similar, providing visual evidence of highly localized spatial and temporal conditions at this scale. Temporal variability in the N-cycling communities versus the stability of their respective potential activities provided evidence of both short-lived temporal niche partitioning and a degree of microbial functional redundancy. Our results indicate that in an unfertilized grassland, at the meter scale, abundances of microbial N-cycling organisms can exhibit transient changes, while N cycling processes remain stable.